
News
Best Tylosin Phosphate Uses Benefits and Side Effects?
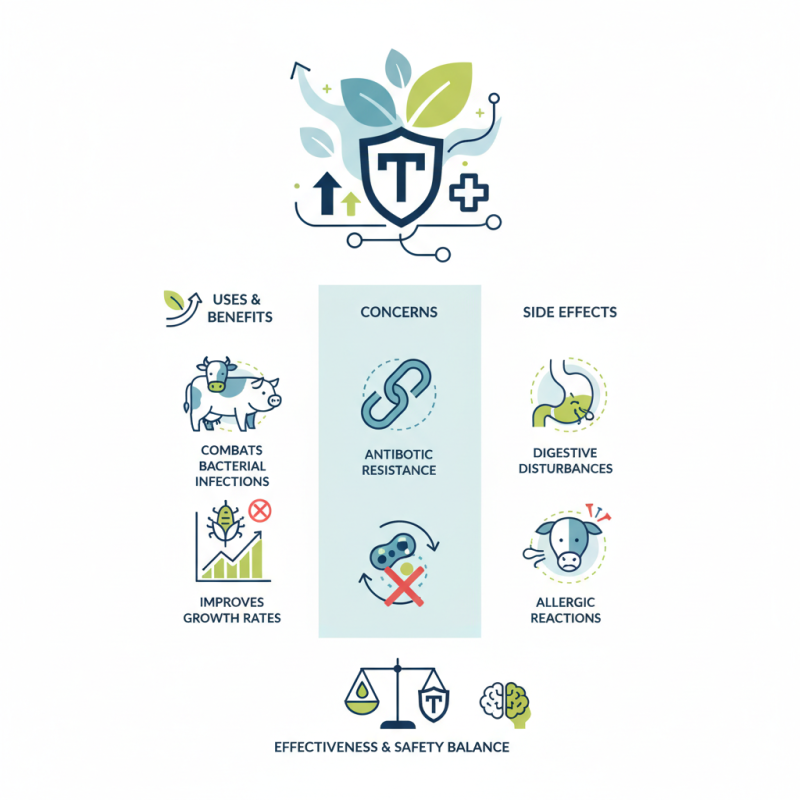
Tylosin Phosphate is an antibiotic widely used in veterinary medicine. It combats various bacterial infections, particularly in livestock. With its effectiveness, many farmers rely on Tylosin Phosphate to ensure animal health.
Tylosin Phosphate benefits go beyond just treating infections. It also helps improve growth rates in animals. This can mean higher yields and better quality products for consumers. However, not everything about this antibiotic is perfect. There are concerns about antibiotic resistance. Some studies suggest the misuse of Tylosin Phosphate may contribute to this issue.
Side effects can occur as well. Animals may experience digestive disturbances or allergic reactions. It is essential to use Tylosin Phosphate responsibly. While it has proven benefits, awareness of potential risks is crucial. Balancing effectiveness and safety should always be a priority for veterinarians and farmers alike.
Best Tylosin Phosphate Applications in Veterinary Medicine

Tylosin phosphate is widely used in veterinary medicine to treat various bacterial infections. It belongs to the macrolide class of antibiotics. Common applications include managing respiratory diseases in cattle, swine, and poultry. This antibiotic effectively reduces respiratory pathogens, promoting better health and productivity.
In sheep and goats, tylosin phosphate addresses foot rot and other infections. It helps control inflammation and speed up recovery. Some veterinarians recommend it for livestock with chronic respiratory issues. However, its use should be monitored closely to avoid potential antibiotic resistance.
Tips: Always follow dosage guidelines provided by veterinarians. Dosage may vary based on animal weight and health status. Monitoring animals after administration is crucial. If side effects occur, seeking professional advice promptly can prevent complications. Ensure clean water and proper nutrition during treatment to support recovery.
Efficacy of Tylosin Phosphate Against Respiratory Infections
Tylosin phosphate is an antibiotic that shows promise against respiratory infections. This compound is known for its broad-spectrum effectiveness. Researchers have noted its impact on bacteria commonly responsible for respiratory ailments. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in these pathogens. This action can lessen symptoms and improve recovery times in affected individuals.
When using tylosin phosphate, it's important to be aware of potential side effects. Some users report gastrointestinal upset or allergic reactions. These issues may be mild but can affect comfort and adherence to treatment. Always monitor your health and consult with a professional if adverse effects arise.
**Tips:**
Ensure proper dosage as recommended. Overuse can lead to resistance. Consider lifestyle factors that might impact respiratory health, such as smoking or allergens. Maintaining a clean environment can support overall well-being. Always reflect on how your choices affect your recovery.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Routes for Tylosin Phosphate
Tylosin phosphate is an important antibiotic used in veterinary medicine. Its primary use is to treat infections caused by specific bacteria in animals. This compound can be administered in various forms, including injectables and powders. The dosage often depends on the species and condition being treated. In general, the recommended dose for livestock is 10-20 mg/kg, administered every 24 hours.
For effective use, it’s crucial to follow administration guidelines. Tylosin can be given orally or through intramuscular injection. Oral administration might require mixing with feed, which can present challenges. Animals may refuse medicated feed, leading to inconsistent dosing. For better management, ensure that the dosage is accurately calculated.
Tips: Always consult a veterinarian to determine the best dosage. Monitor the animal for any adverse reactions. If side effects arise, discontinue use immediately. Tylosin can cause gastrointestinal disturbances in some cases, including diarrhea and vomiting.
For poultry, the treatment duration usually lasts from 3 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection. There's room for adjustment based on individual responses. Keep in mind that resistance can develop if Tylosin is overused. Regular assessment of treatment effectiveness is essential.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Tylosin Use
Tylosin is an antibiotic that can treat infections in animals. It’s important to be aware of potential side effects. Common effects include diarrhea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Some animals may also experience drowsiness or lethargy. These symptoms may indicate an adverse reaction to the drug.
There are risks associated with its use. Allergic reactions could manifest as skin rashes or swelling. In severe cases, anaphylaxis may occur. Monitoring is crucial, especially in sensitive animals. Dosage should be adjusted carefully to prevent toxicity. Long-term use may lead to antibiotic resistance. It’s essential to weigh the benefits against these risks when considering tylosin treatment.
Consulting a veterinarian is advised. They can provide guidance based on the specific health needs of the animal. Awareness of side effects encourages responsible use of antibiotics. It fosters a more thoughtful approach to animal health and welfare.
Regulatory Considerations for Tylosin Phosphate in Animal Health
Tylosin phosphate plays a crucial role in animal health, particularly in livestock. Its regulatory considerations are vital for safe use. This antibiotic is primarily used to treat respiratory and gastrointestinal infections in animals. However, proper guidelines must be followed to avoid misuse.
Regulatory agencies have specific requirements for tylosin phosphate administration. It's essential to ensure that dosages are appropriate to prevent antibiotic resistance. Farmers and veterinarians should be aware of these guidelines to protect animal welfare. Misuse can lead to treatment failures and harmful side effects. Continuous education on these regulations is key.
Monitoring the impact of tylosin is necessary for sustainable practices. Researchers must evaluate its long-term effects on various species. Ensuring compliance with regulations fosters a healthier environment. Regular assessment can reveal areas of improvement. Ongoing dialogue among experts can address concerns effectively.
Related Posts
-

Understanding Tylosin Phosphate: Revolutionizing Antibiotic Use in Livestock Health
-

Mastering the Essentials of Best Tylosin Phosphate for Global Procurement Success
-

Essential Checklist for Sourcing High-Quality Tylosin Phosphate: What You Need to Know
-

How to Use Tylosin Phosphate for Optimal Animal Health and Production
-

Unlocking the Power of Agmatine Sulfate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Benefits and Uses
-

7 Essential Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of Cefotaxime Sodium in Your Treatment Protocols





